Forex trading revolves around the buying and selling of currencies, which are traded in pairs. Each currency pair represents the exchange rate between two currencies, and understanding how these pairs work is fundamental to becoming a successful Forex trader. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of currency pairs, the different types of pairs available, how to read and analyze them, and strategies for trading various currency pairs. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, this guide will provide valuable insights into the intricacies of currency pairs.

1. Introduction to Currency Pairs
In the Forex market, currencies are always traded in pairs. This is because, in every foreign exchange transaction, you are simultaneously buying one currency and selling another. A currency pair shows how much of one currency (the quote currency) is needed to purchase one unit of another currency (the base currency). Understanding how currency pairs function is essential for making informed trading decisions and managing risk effectively.
2. How Currency Pairs Work
Currency pairs are quoted in a specific format that indicates the value of one currency relative to another. This format includes the base currency, the quote currency, the bid price, and the ask price.
Base Currency and Quote Currency
The base currency is the first currency listed in a currency pair, while the quote currency is the second. The value of the base currency is always 1, and the quote currency shows how much of it is required to purchase one unit of the base currency.
Example: In the currency pair EUR/USD, the euro (EUR) is the base currency, and the U.S. dollar (USD) is the quote currency. If the EUR/USD is quoted at 1.20, it means that 1 euro is equal to 1.20 U.S. dollars.
Bid and Ask Prices
Currency pairs are quoted with two prices: the bid price and the ask price. The bid price is the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay for the base currency, while the ask price is the lowest price that a seller is willing to accept.
Example: If the EUR/USD pair is quoted with a bid of 1.2050 and an ask of 1.2052, traders can sell euros at 1.2050 (the bid price) or buy euros at 1.2052 (the ask price).
Understanding Pips and Spreads
A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price move that can occur in a currency pair. For most currency pairs, a pip is the fourth decimal place (0.0001). The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices, representing the cost of trading a currency pair.
Example: If the bid price for EUR/USD is 1.2050 and the ask price is 1.2052, the spread is 2 pips (1.2052 – 1.2050 = 0.0002).
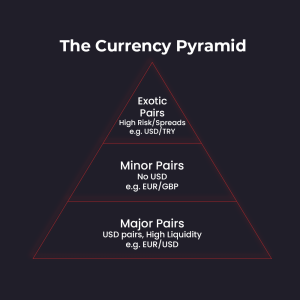
3. Types of Currency Pairs
Currency pairs are generally categorized into three types: major pairs, minor pairs, and exotic pairs. Each type has unique characteristics and trading dynamics.
Major Currency Pairs
Major currency pairs consist of the most traded currencies in the world, paired with the U.S. dollar. These pairs are highly liquid, meaning they have tight spreads and are less prone to volatile swings.
Examples:
EUR/USD (Euro/U.S. Dollar)
USD/JPY (U.S. Dollar/Japanese Yen)
GBP/USD (British Pound/U.S. Dollar)
USD/CHF (U.S. Dollar/Swiss Franc)
Ready to Start Trading?
With G2G Group LTD, creating your account and withdrawing funds becomes much easier. This allows you to seamlessly navigate the complex landscape of the Forex trading sector without any hassles.
Minor Currency Pairs
Minor currency pairs, also known as cross-currency pairs, do not include the U.S. dollar. These pairs are still relatively liquid but may have wider spreads compared to major pairs.
Examples:
EUR/GBP (Euro/British Pound)
EUR/AUD (Euro/Australian Dollar)
GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen)
Exotic Currency Pairs
Exotic currency pairs involve one major currency paired with a currency from a smaller or emerging economy. These pairs are less liquid, more volatile, and have wider spreads compared to major and minor pairs.
Examples:
USD/TRY (U.S. Dollar/Turkish Lira)
USD/SEK (U.S. Dollar/Swedish Krona)
EUR/HKD (Euro/Hong Kong Dollar)
Ready to Start Trading?
With G2G Group LTD, creating your account and withdrawing funds becomes much easier. This allows you to seamlessly navigate the complex landscape of the Forex trading sector without any hassles.

4. Factors Influencing Currency Pairs
Several factors influence the movement of currency pairs, including economic indicators, interest rates, and political events. Understanding these factors can help traders anticipate price movements and make informed trading decisions.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment data, and inflation rates provide insights into the health of a country’s economy. Positive economic data can strengthen a currency, while negative data can weaken it.
Example: If the U.S. releases strong employment data, the USD might strengthen against other currencies, causing pairs like EUR/USD to move lower.
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by central banks are one of the most influential factors in Forex trading. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign investment, boosting demand for the currency, while lower rates can have the opposite effect.
Example: If the European Central Bank raises interest rates, the EUR might appreciate against other currencies, leading to an increase in the EUR/USD pair.
Political and Geopolitical Events
Political stability and geopolitical events can have significant impacts on currency pairs. Elections, trade agreements, and conflicts can cause volatility and rapid price changes in the Forex market.
Example: During the Brexit referendum, the GBP/USD pair experienced extreme volatility as traders reacted to the uncertainty surrounding the outcome.
5. How to Read and Analyze Currency Pairs
Analyzing currency pairs involves both technical and fundamental analysis. Understanding how to read charts, use indicators, and assess economic conditions is crucial for successful trading.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis focuses on studying historical price movements to predict future trends. Traders use charts, patterns, and technical indicators to identify trading opportunities.
Example: A trader might use a moving average crossover strategy to identify potential entry points in the EUR/USD pair. If the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average, it could signal a buying opportunity.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating economic data, interest rates, and other macroeconomic factors to determine the value of a currency. This type of analysis helps traders understand the underlying factors driving currency prices.
Example: A trader might analyze the U.S. Federal Reserve’s interest rate policy to anticipate movements in the USD/JPY pair. If the Fed signals an upcoming rate hike, the trader might expect the USD to strengthen.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis gauges the overall mood of the market, whether traders are bullish or bearish on a
particular currency pair. Tools like the Commitment of Traders (COT) report can help traders understand market sentiment.
Example: If the COT report shows that a majority of traders are long on the EUR/USD pair, it might indicate bullish sentiment, leading the trader to consider a long position.
Ready to Start Trading?
With G2G Group LTD, creating your account and withdrawing funds becomes much easier. This allows you to seamlessly navigate the complex landscape of the Forex trading sector without any hassles.

6. Strategies for Trading Currency Pairs
Different currency pairs require different trading strategies based on their characteristics, volatility, and the trader’s goals. Here are some common strategies for trading currency pairs:
Trend Following
Trend following involves identifying and trading in the direction of the prevailing market trend. This strategy works well with major currency pairs, which tend to follow more predictable trends due to their high liquidity.
Example: A trader might identify an uptrend in the USD/JPY pair by observing higher highs and higher lows on the daily chart. The trader would then look for opportunities to buy during pullbacks.
Range Trading
Range trading involves identifying key support and resistance levels where a currency pair’s price tends to fluctuate. Traders buy at support and sell at resistance, capitalizing on the range-bound nature of the market.
Example: If the EUR/GBP pair is trading within a range of 0.8500 to 0.8700, a range trader might buy near 0.8500 and sell near 0.8700, repeating this process as long as the range holds.
Breakout Trading
Breakout trading involves entering a trade when the price breaks out of a defined support or resistance level, signaling the start of a new trend. This strategy can be effective with both major and minor currency pairs.
Example: If the GBP/USD pair has been consolidating within a narrow range and then breaks above resistance at 1.4000, a breakout trader might enter a long position, anticipating further upward movement.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Trading Currency Pairs
Trading currency pairs can be profitable, but it’s important to avoid common mistakes that can lead to losses.
Ignoring Correlations
Currency pairs are often correlated, meaning they move in the same direction or opposite directions. Ignoring these correlations can lead to overexposure to risk.
Example: If a trader is long on both EUR/USD and GBP/USD, they are effectively doubling their exposure to the U.S. dollar. If the USD strengthens, both trades could result in losses.
Overtrading Multiple Pairs
Trading too many currency pairs at once can lead to confusion, lack of focus, and overexposure to risk. It’s better to concentrate on a few pairs and thoroughly analyze them.
Example: A trader who tries to monitor and trade ten different currency pairs might miss important signals or make mistakes due to the sheer volume of information to process.
Neglecting Economic News
Economic news releases can cause significant volatility in the Forex market. Failing to stay informed about upcoming news events can lead to unexpected losses.
Example: A trader might hold a position in the USD/CAD pair without realizing that a major Canadian economic report is about to be released. A negative report could cause the CAD to weaken sharply, leading to losses.
8. Conclusion: Mastering Currency Pairs for Forex Success
Understanding currency pairs is fundamental to success in Forex trading. By grasping the mechanics of how currency pairs work, recognizing the factors that influence them, and employing effective trading strategies, you can navigate the Forex market with greater confidence and precision. Whether you prefer trading major, minor, or exotic currency pairs, mastering the nuances of these pairs will enhance your ability to make informed decisions, manage risk, and achieve your trading goals.
